Emerging AI design patterns. Part 1
April 1st, 2025
AI is the next big step in computing after Web and Mobile. Like previous major technology shifts, it significantly changes the way people interact with digital products.
Over the past two years, we’ve seen an evolution from basic chat interfaces to a whole range of AI-first products with innovative design patterns that assist users in both work and everyday tasks.
This article documents ongoing changes and how they make AI accessible to a broader audience. Today we’ll explore the first 10 AI design patterns, followed by another 10 in Part 2.
Prompt examples
Most users might find it too confusing to see just a blank page in front of them and not know where to start. Prompt examples are shortcuts that help guide people, streamline workflows, and provide an overview of the tool's capabilities.
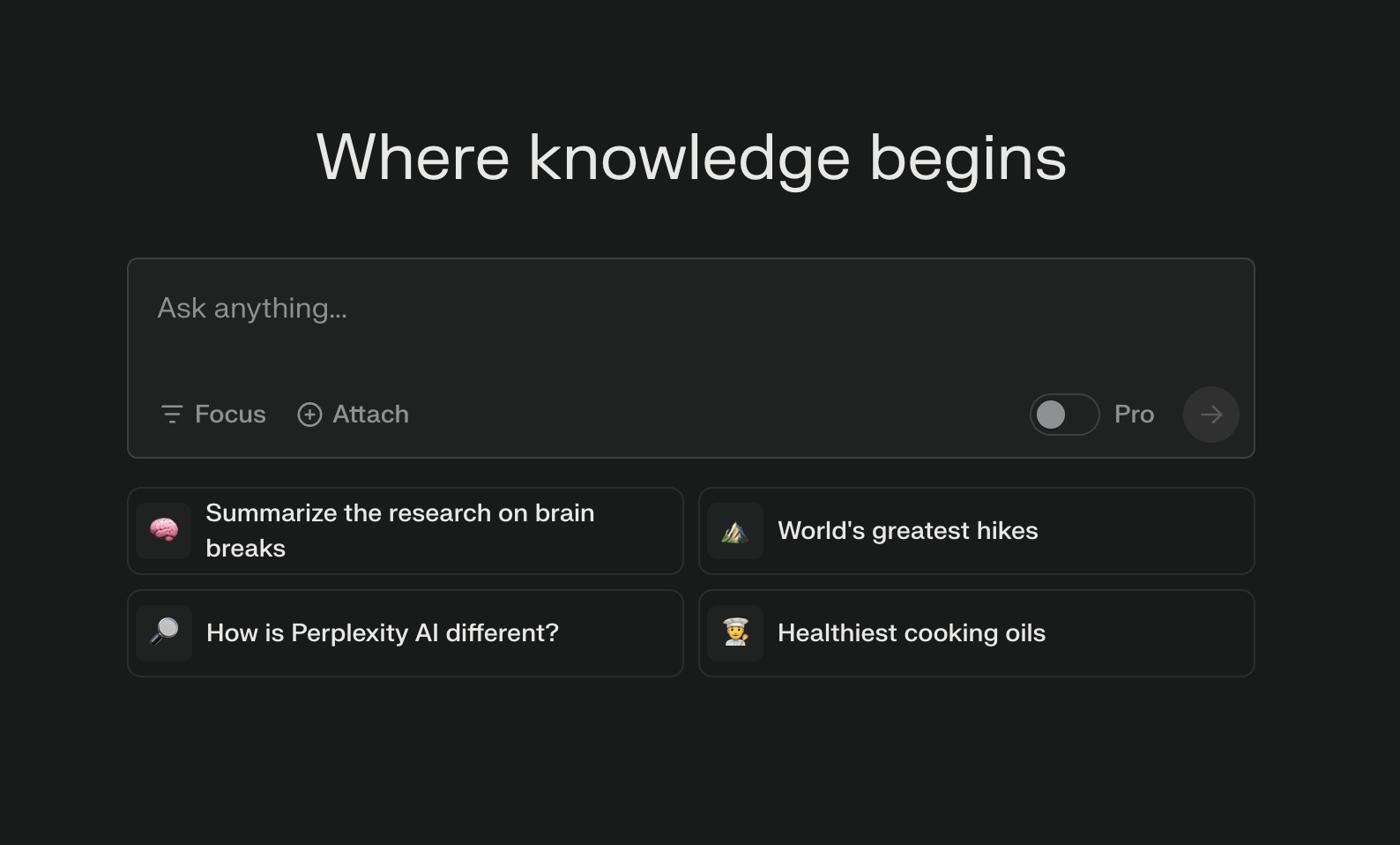 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Figjam
Figjam
 ElevenLabs
ElevenLabs
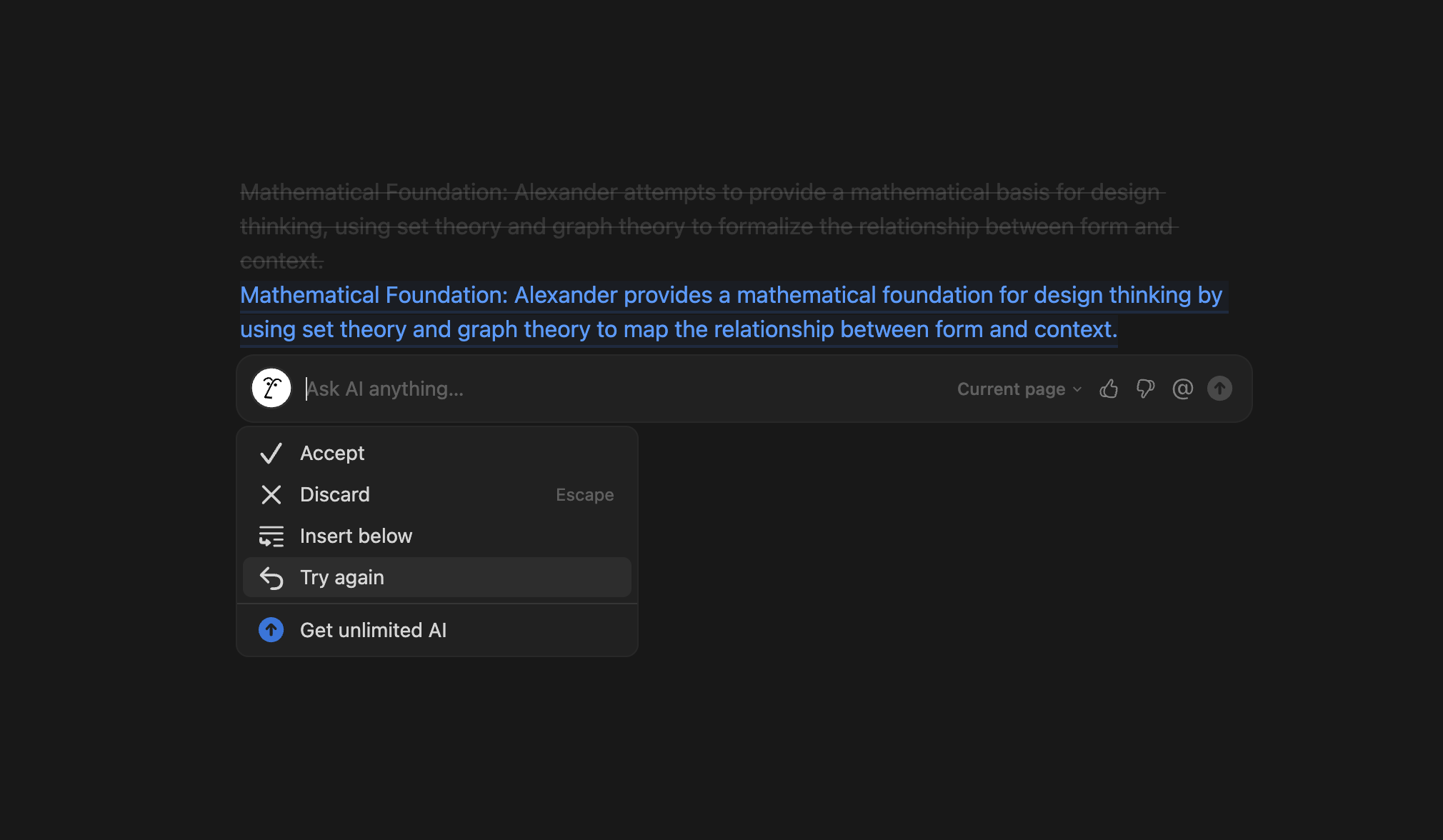
Regenerate/Try again
Hallucinations remain one of the significant challenges in generative AI so one can’t be sure of the result. A regeneration feature serves two crucial purposes: it allows users to start over when the AI significantly misinterprets the request and it enables exploration of alternative solutions from the same prompt. Users often can toggle between different results and choose the most appropriate one.
 Notion
Notion
 Claude
Claude
Refine output
Getting a correct result on the first attempt when working with AI tools is rarely possible. Some tools might offer a list of common actions that help users iterate on results by selecting instead of writing prompts from scratch every time.
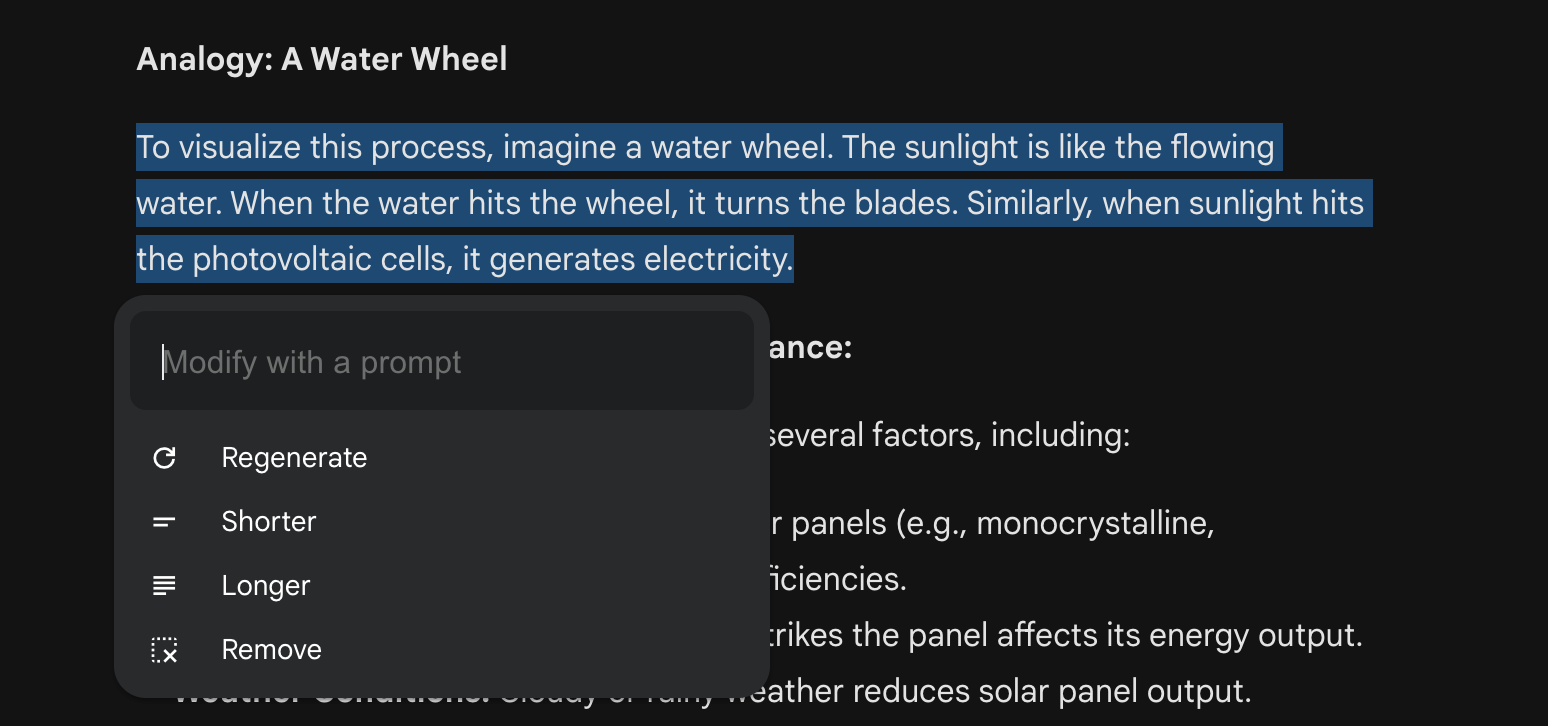 Gemini
Gemini
 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Figma Slides
Figma Slides
Inpainting
It is a concept similar to “Refine output” but for images or videos. Users can select an area and replace it with something new.
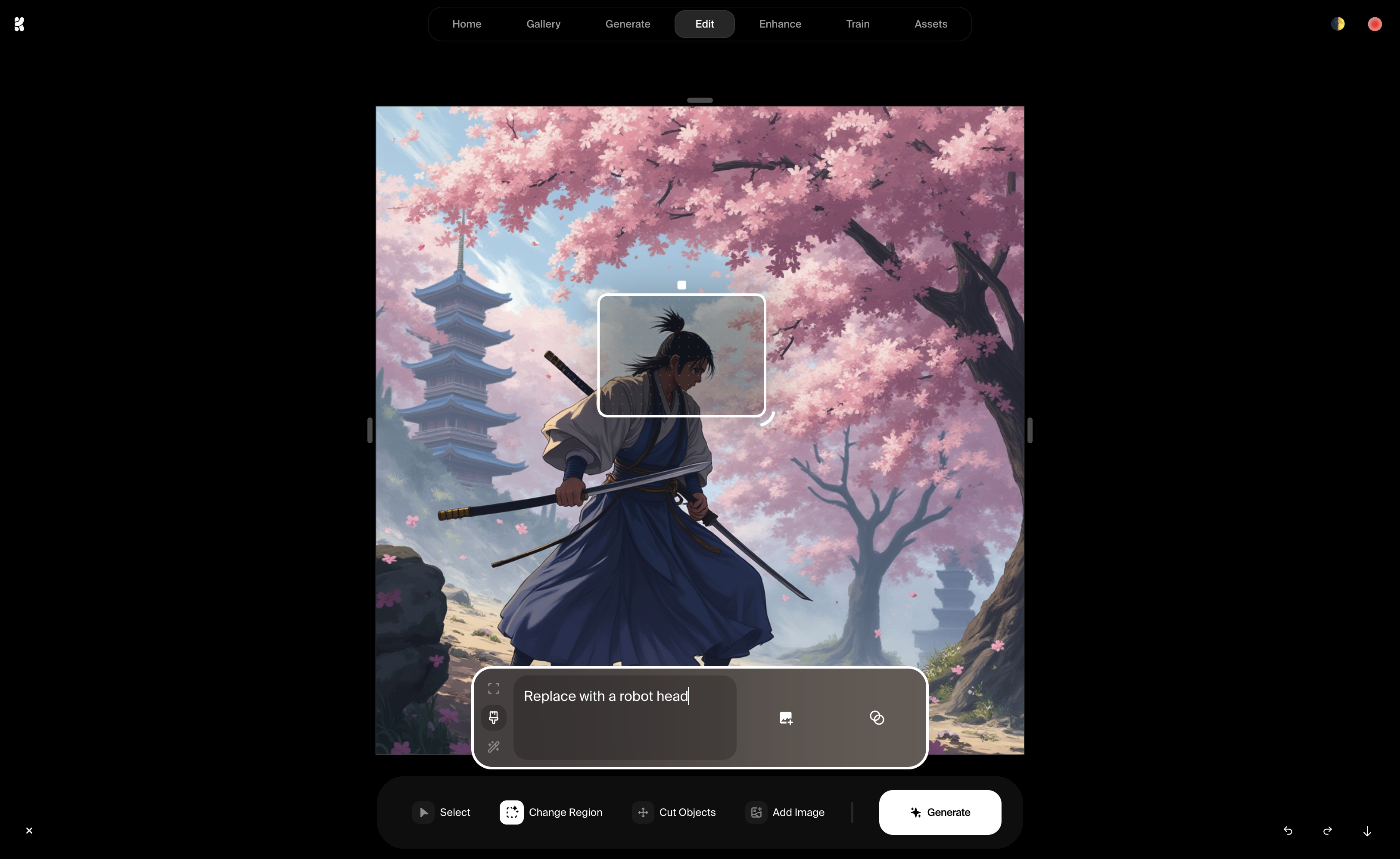
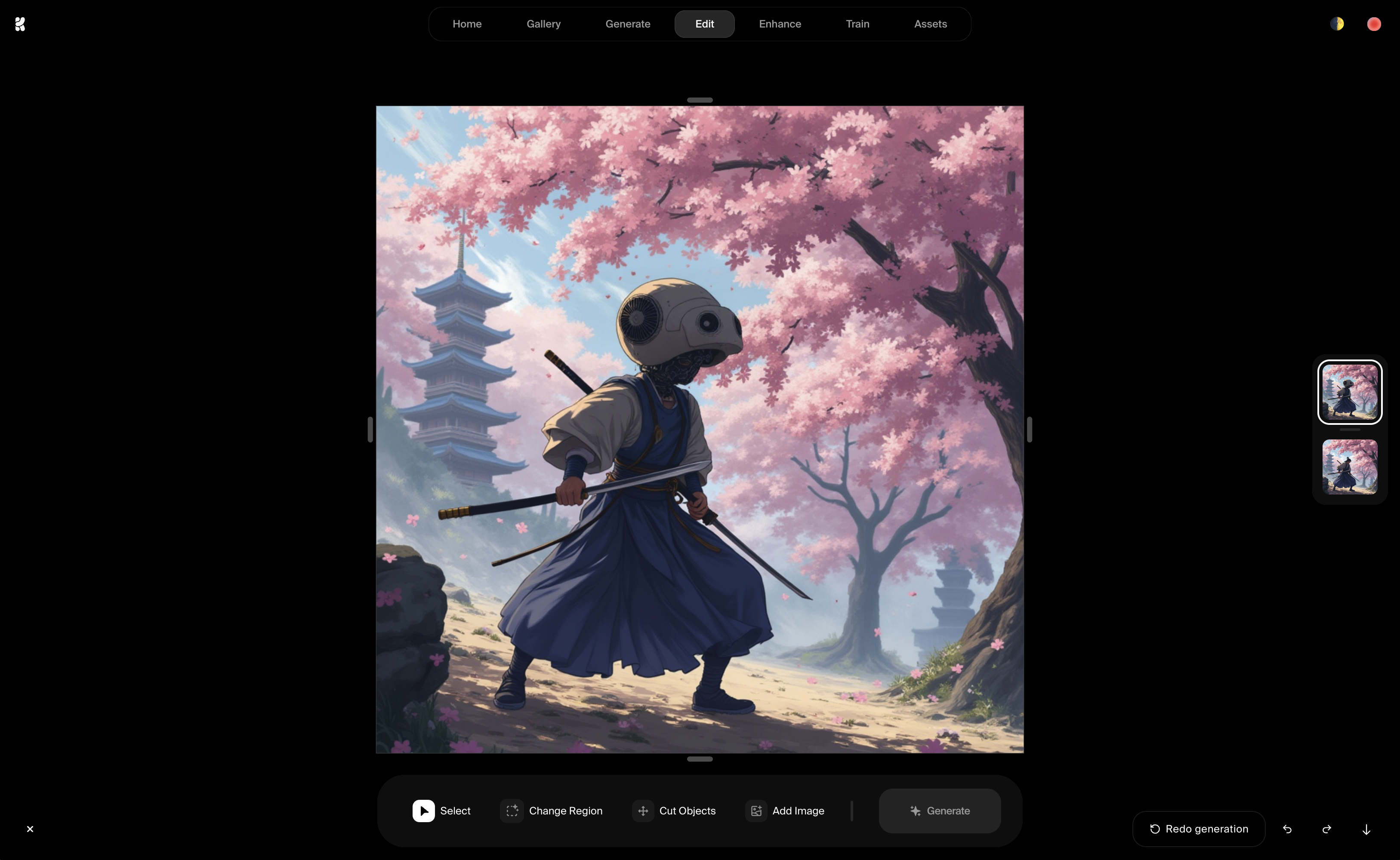 Krea
Krea
Stop generation
Complex prompts can take significant time to complete. Giving users control to interrupt generation if needed is essential for efficiency. It allows users to accept a satisfactory partial result or stop an obviously incorrect generation earlier to save time.
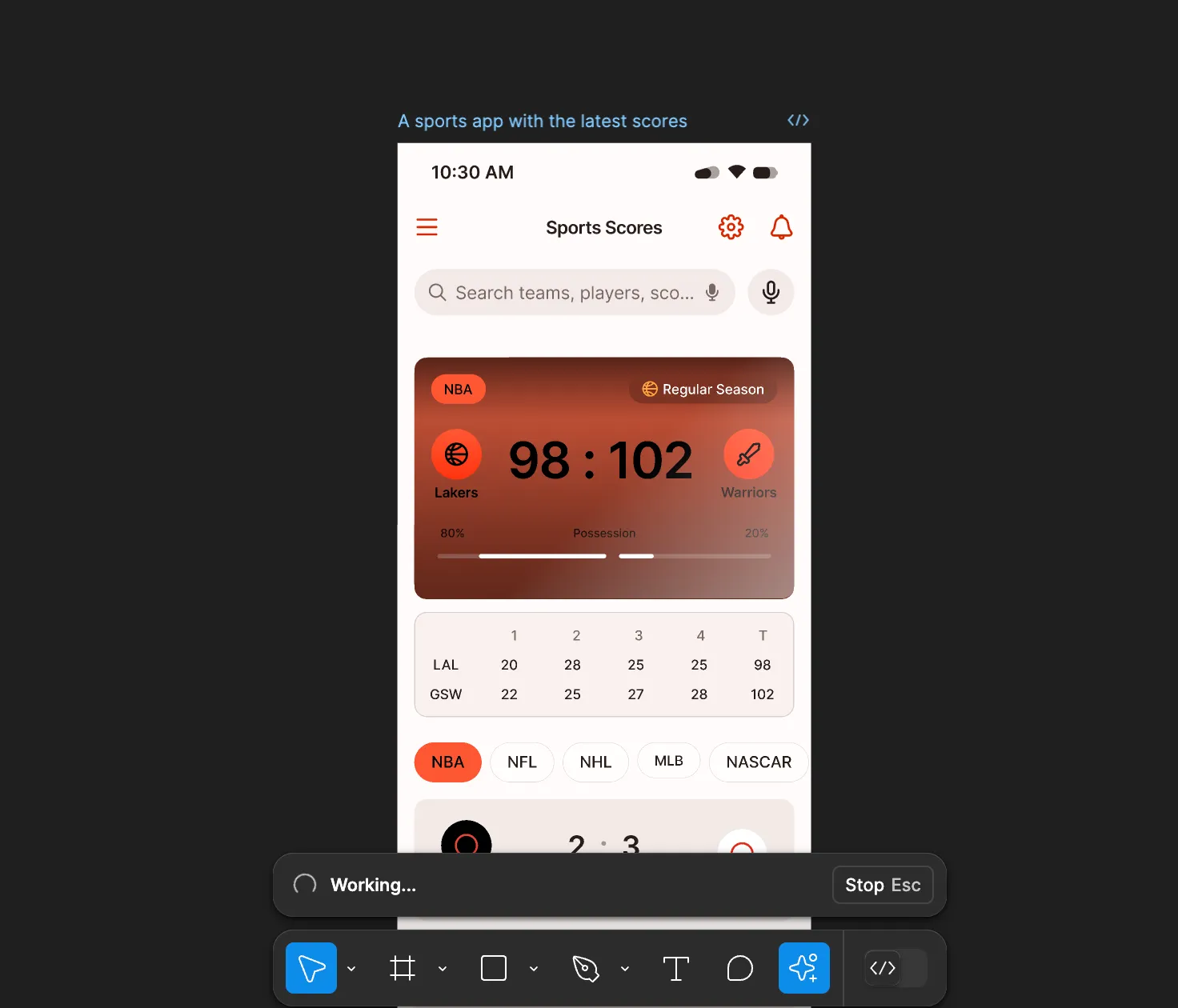 Figma
Figma
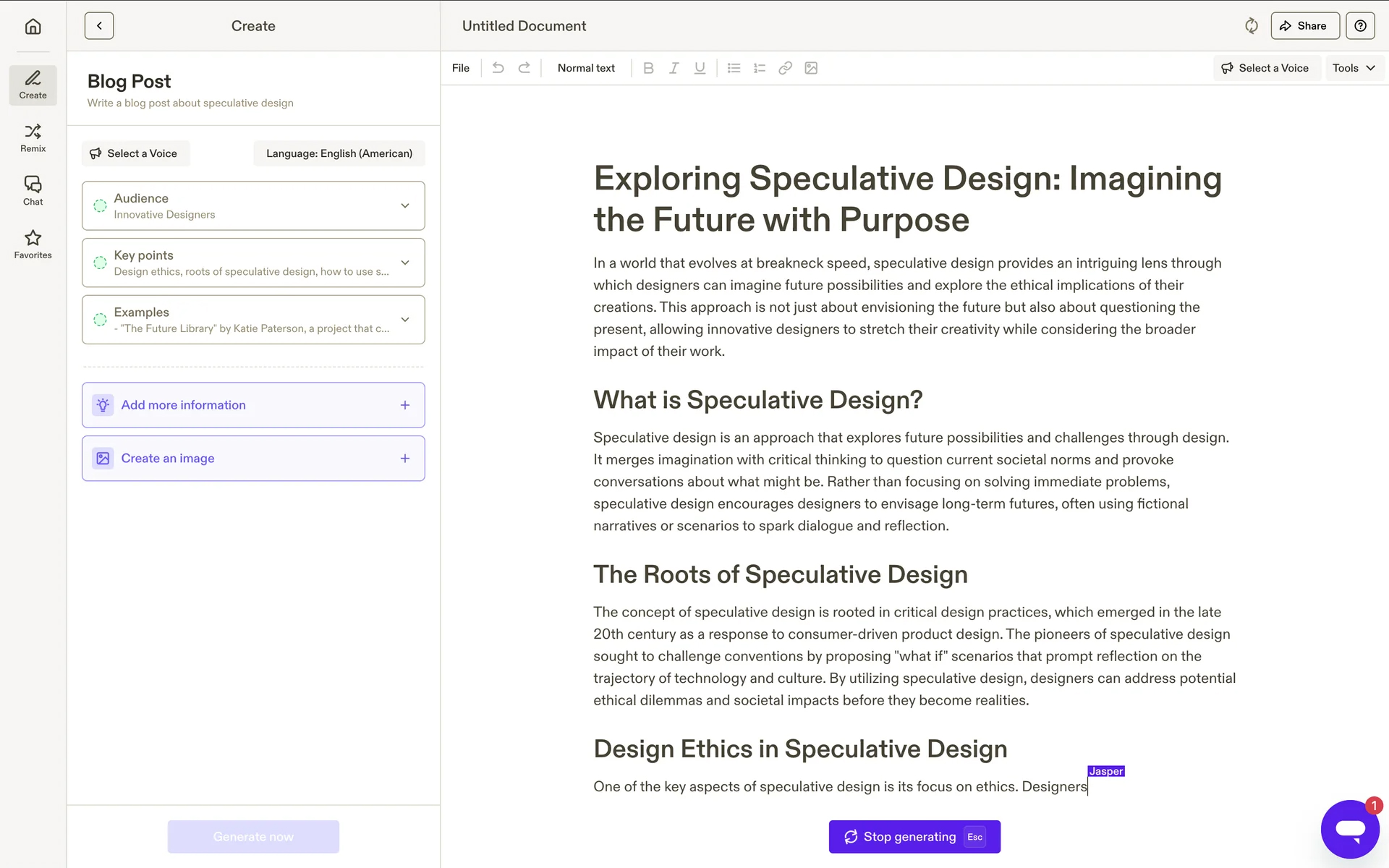 Jasper
Jasper
Multiple outputs/Variations
Generating multiple outputs simultaneously makes working with content much faster (especially for images and videos). The ability to compare different variations side by side helps to narrow down and choose the most promising direction for further iterations.
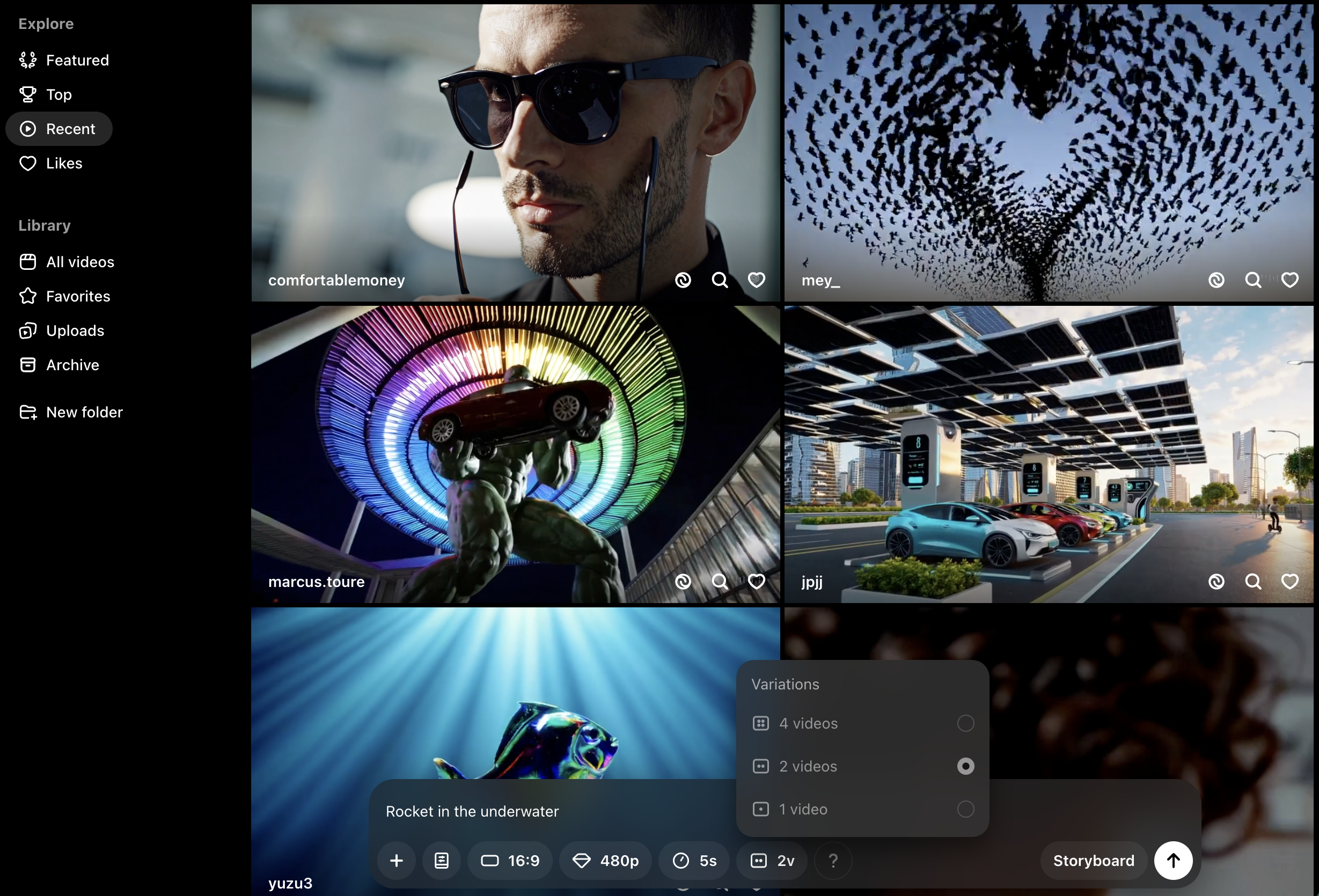 Sora
Sora
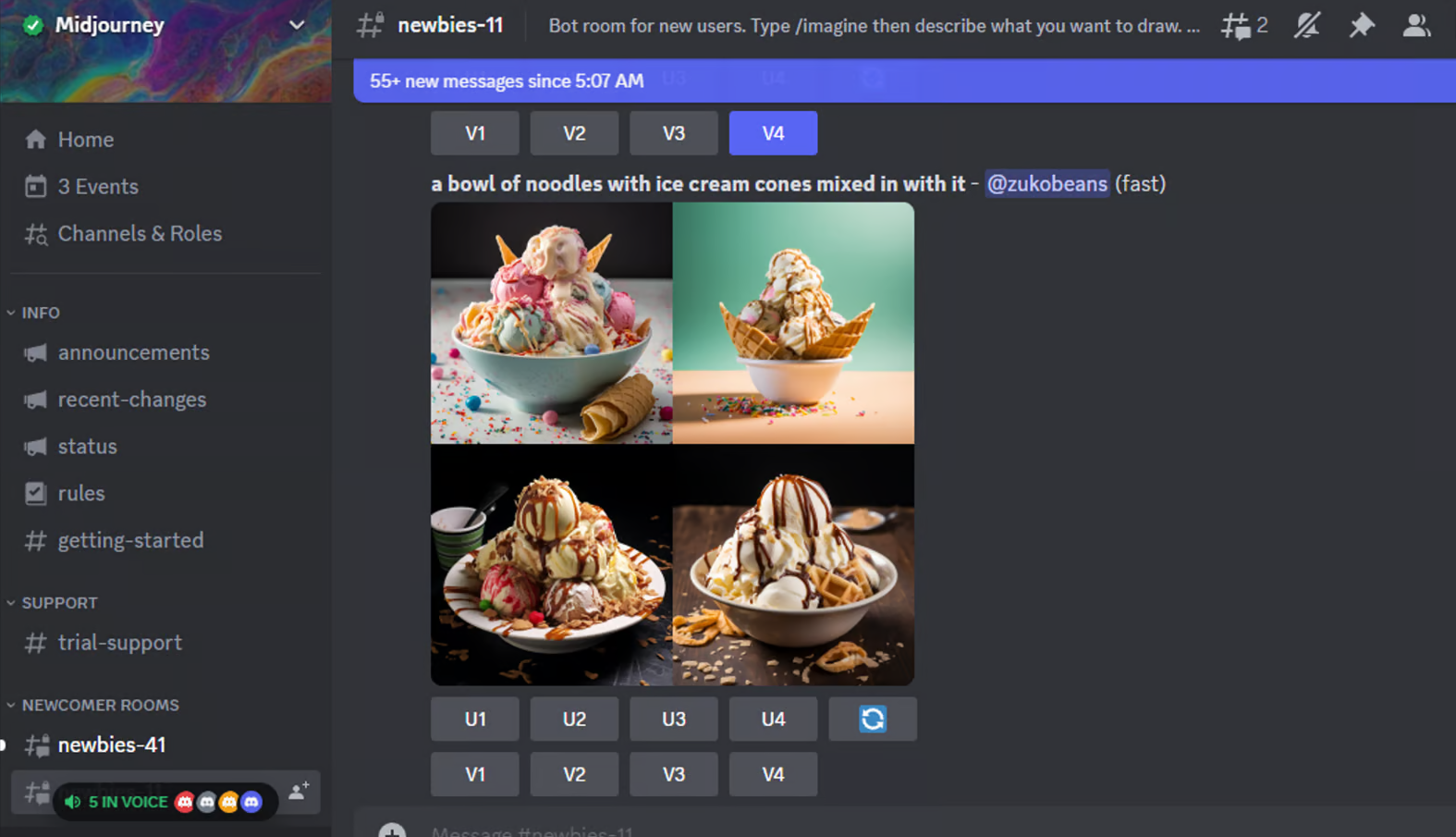 Midjourney
Midjourney
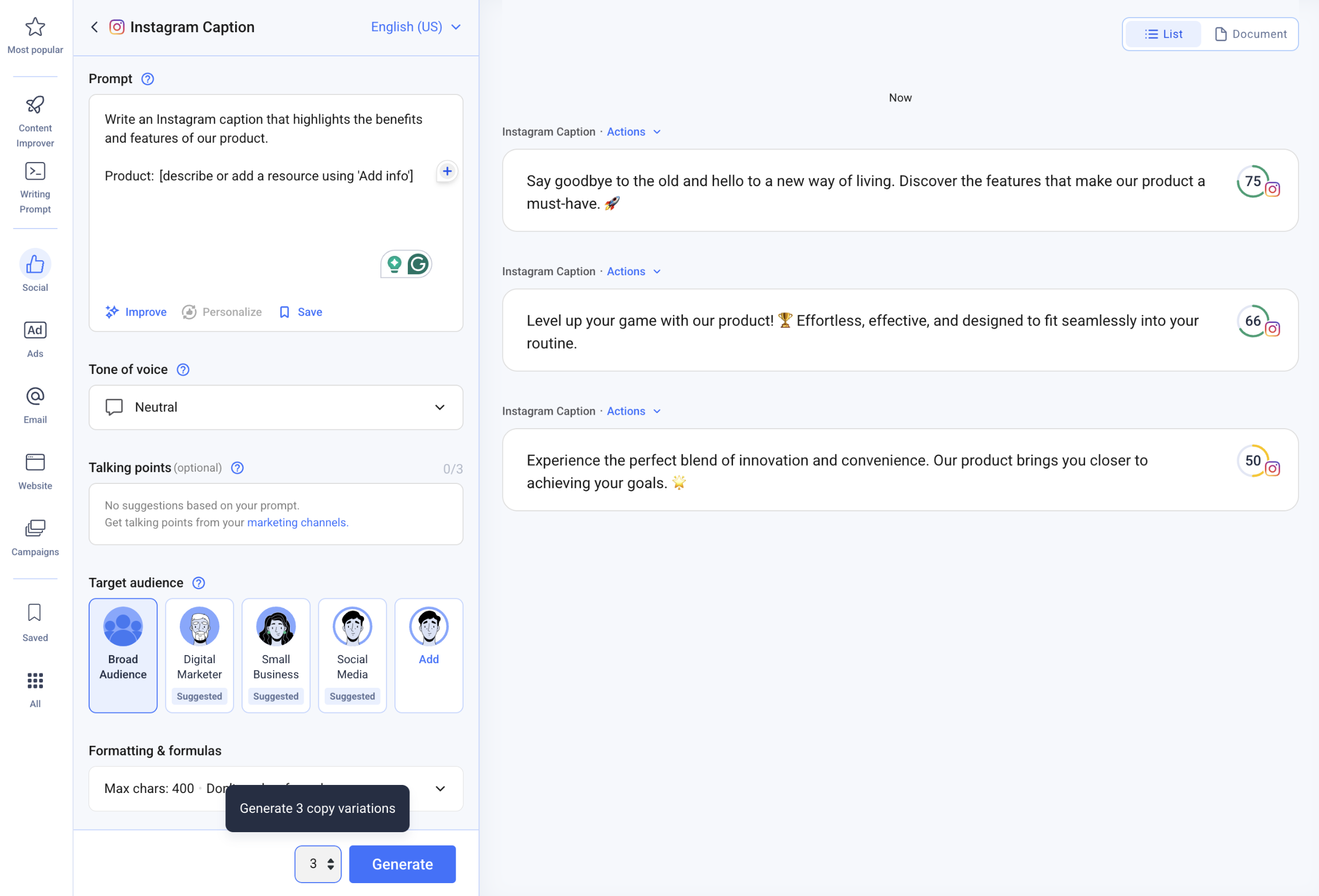 Anyword
Anyword
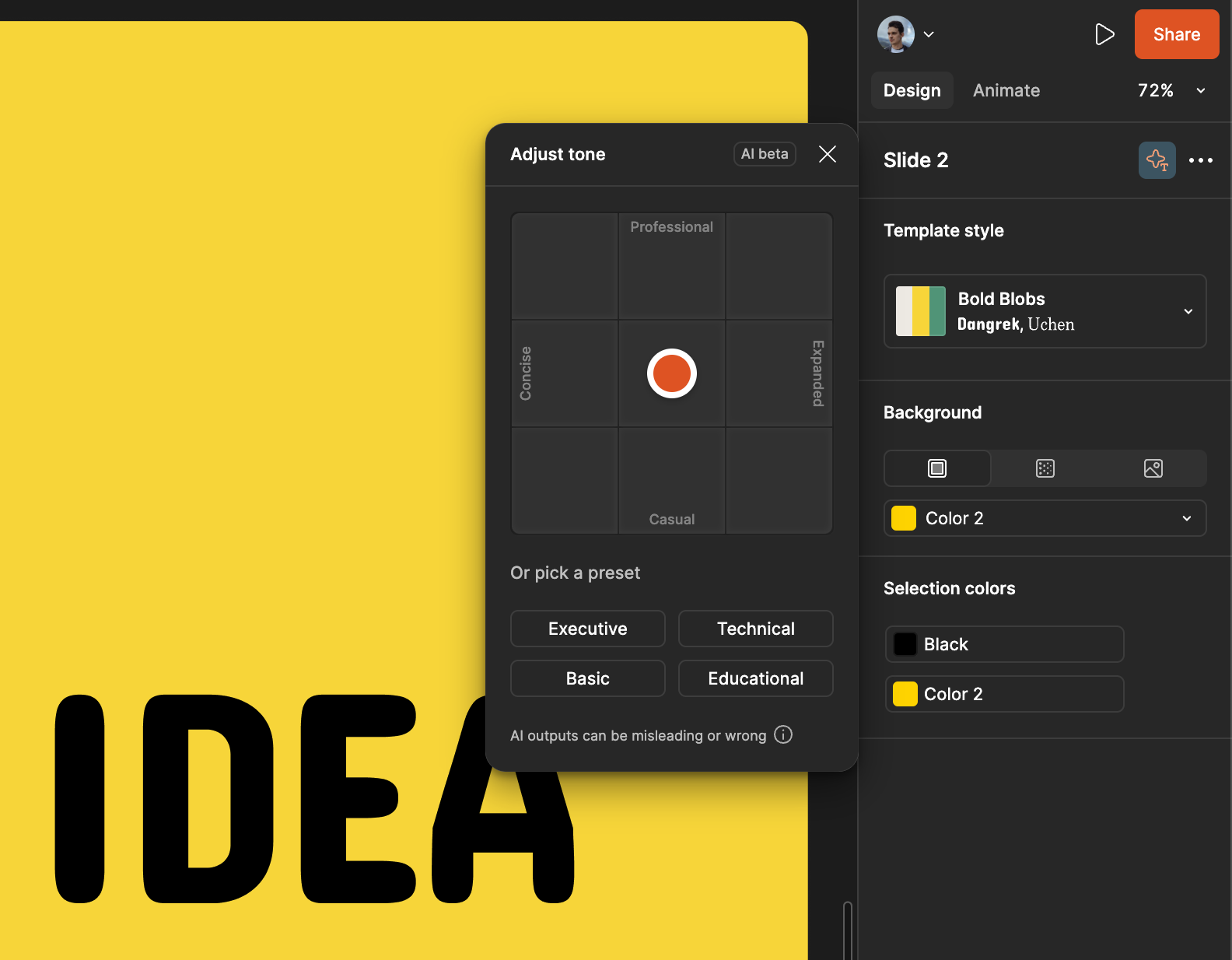
Temperature/creativity
Temperature controls the randomness in AI outputs. The higher the temperature, the more creative and diverse the generated text/image/content will be. If this parameter is low, the result will be much more straightforward and predictable. The typical pattern is to allow users to adjust the temperature via a slider, giving them direct control over the balance between creativity and consistency.
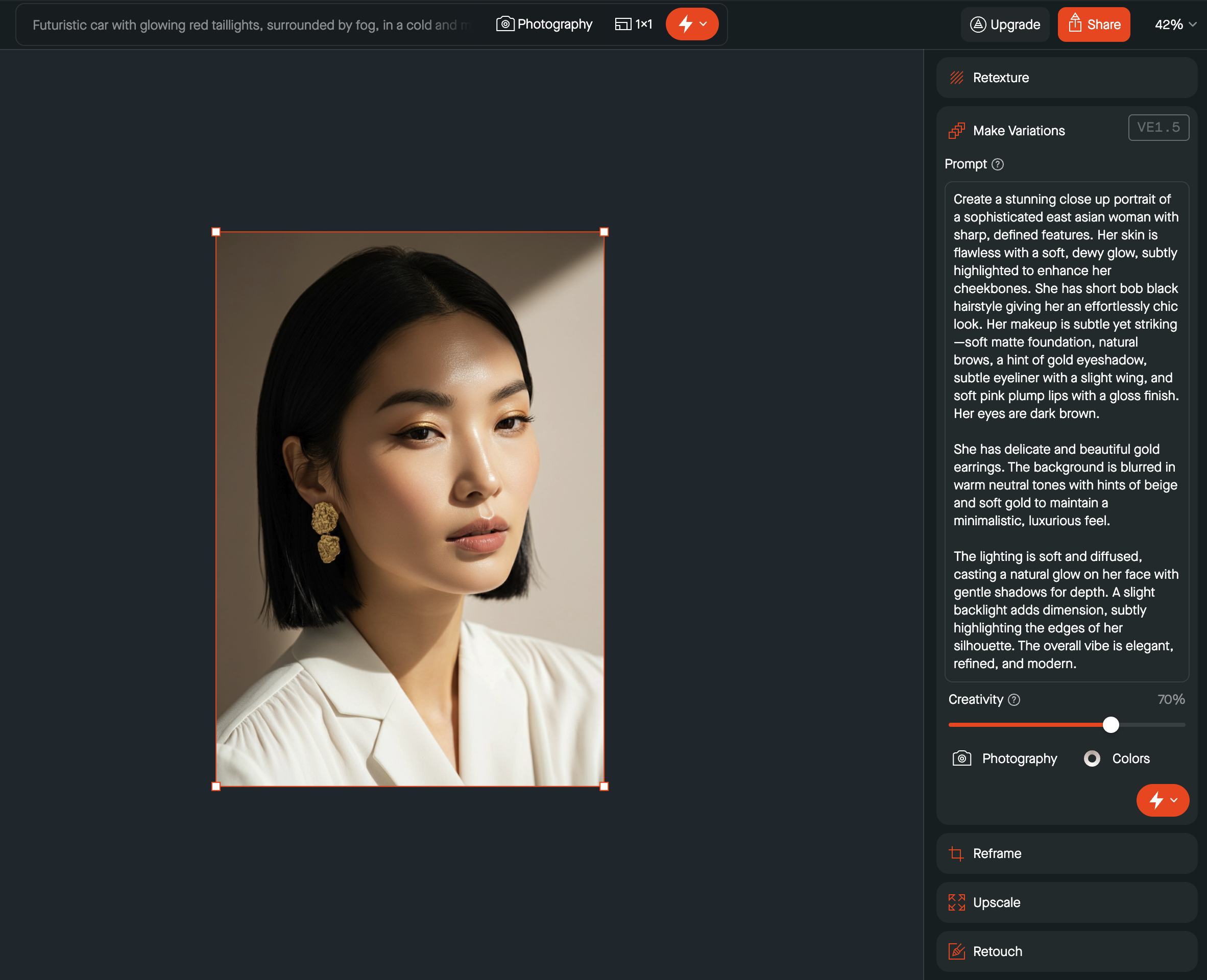 Visual Electric
Visual Electric
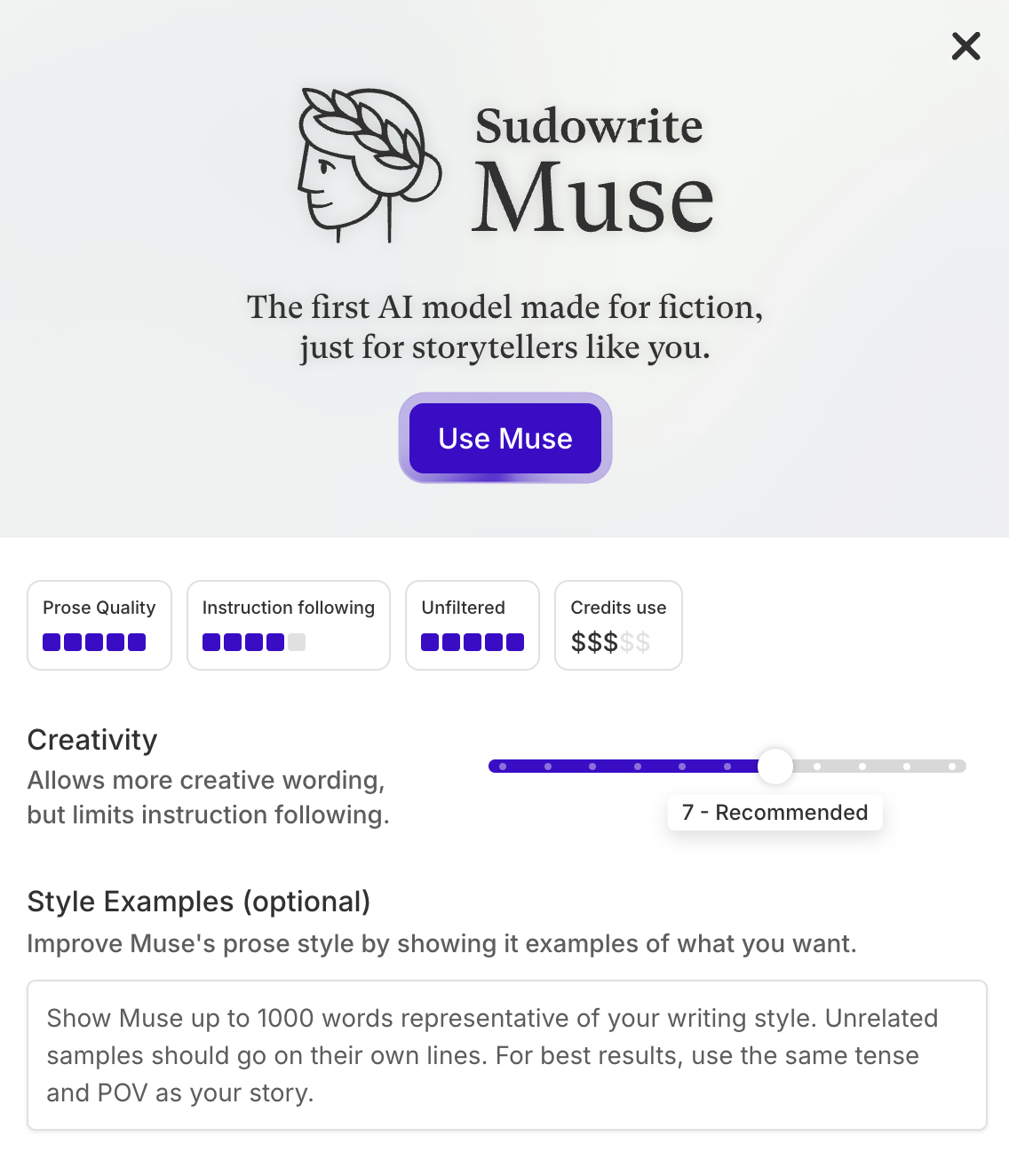 Sudowrite
Sudowrite
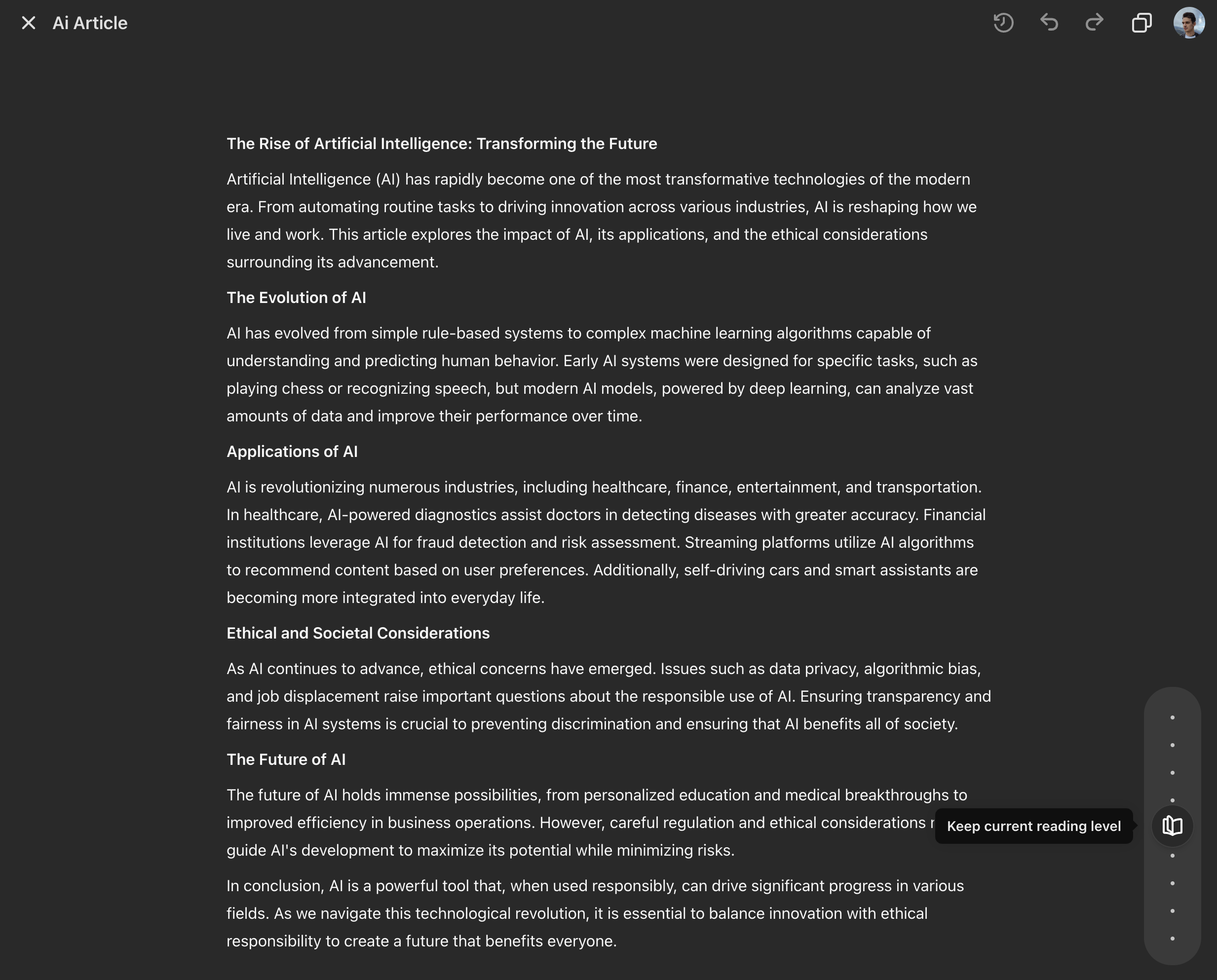
Summarize
One of the most useful generative AI features is analyzing large chunks of information and creating a distilled version with key points. However, it’s important to allow users to easily review the original text and be aware that the summary might lack some critical information. To make it more personalized, AI apps can provide some control over the summary’s length and format (for example, bullet points or short paragraphs).
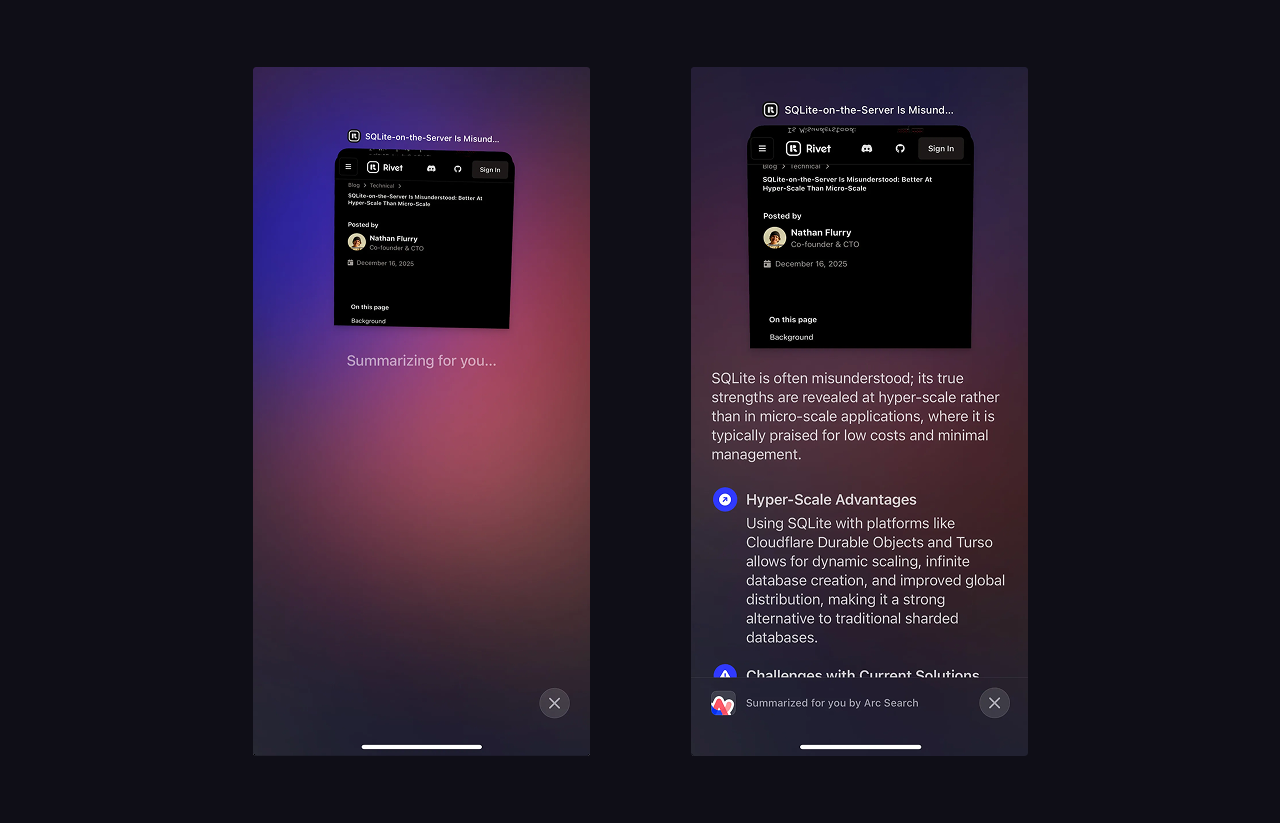 Pinch to summarize in Arc Search
Pinch to summarize in Arc Search
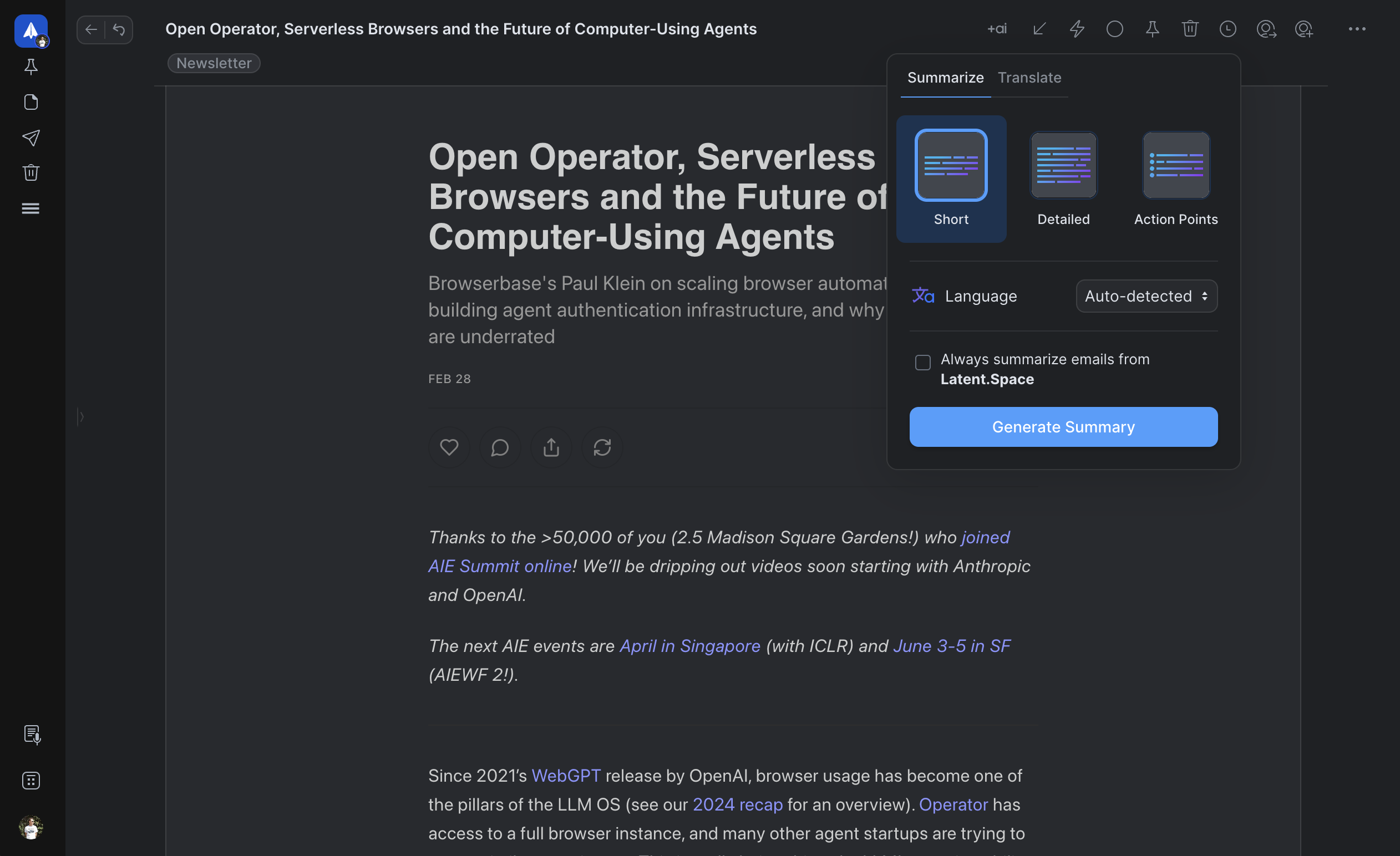 Spark Mail
Spark Mail
Auto-generated content
Some AI products go one step further and auto-generate summaries and headlines from existing content, eliminating extra clicks for users.
 Cora
Cora
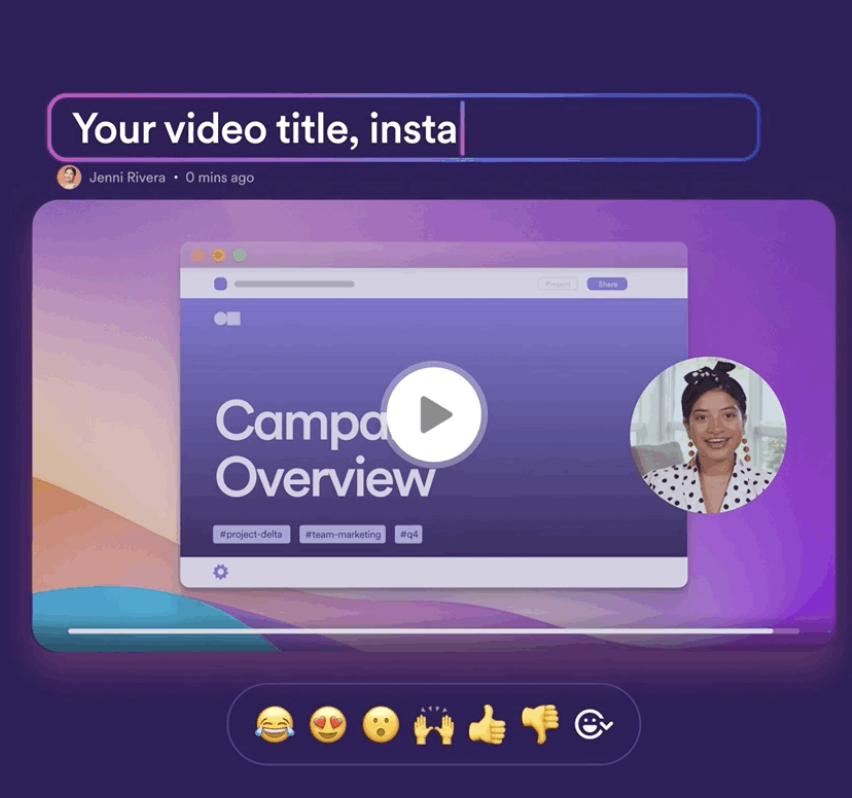 Loom autogenerates title after the recording
Loom autogenerates title after the recording
Describe process/thinking
For complex or lengthy tasks, AI can first generate a step-by-step plan and optionally await user approval before execution. This approach provides observability and confidence over the future result and also leaves space to make necessary changes. In addition, showing how the AI thinks works like a loader, making the wait feel shorter when the response isn’t instant.
 Perplexity
Perplexity
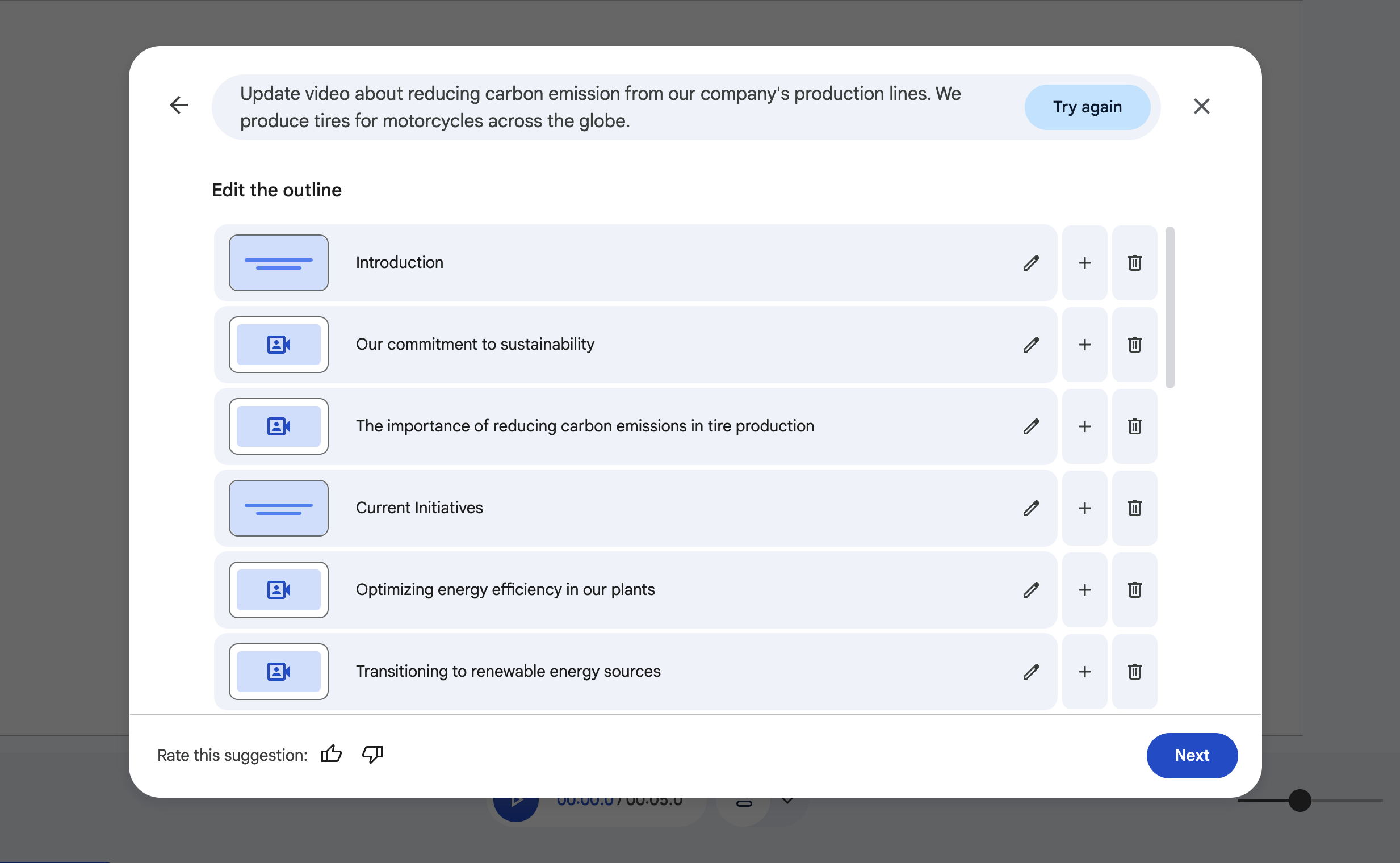 Google Vids
Google Vids
Prompt feedback
The average user isn’t very good at prompting or articulating clearly all the details of the output they want to get. So providing immediate tips and feedback on prompts can explain what should be changed to get better results. Alternatively, AI tools can achieve a similar effect by asking clarifying questions before generating the final response.
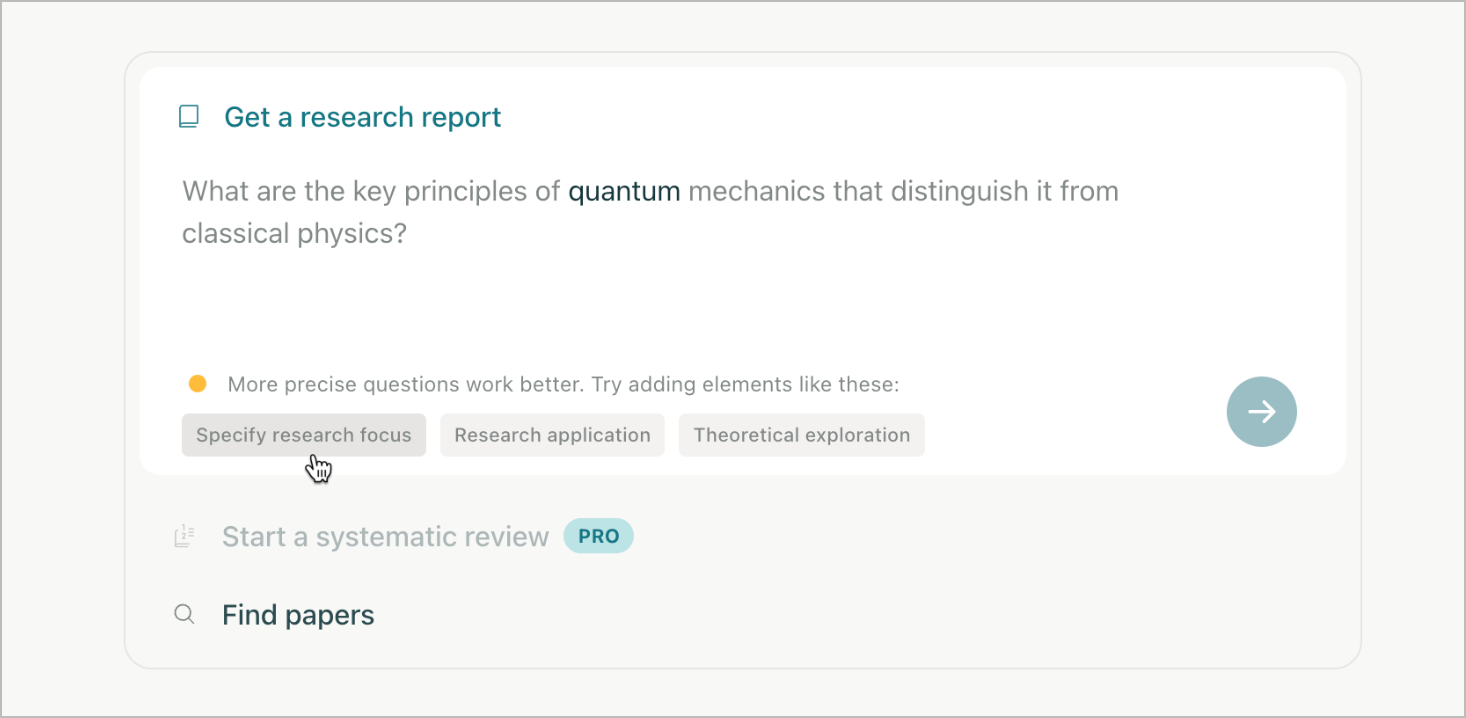 Elicit
Elicit
Select model
Nowadays AI models have complex names and users may not understand their differences. This makes choosing the right model difficult. To help people make informed decisions, it's important to clearly explain each model's capabilities, ideal use cases, and limitations. In the future, we can expect tools to automatically select the best model based on the user’s task.
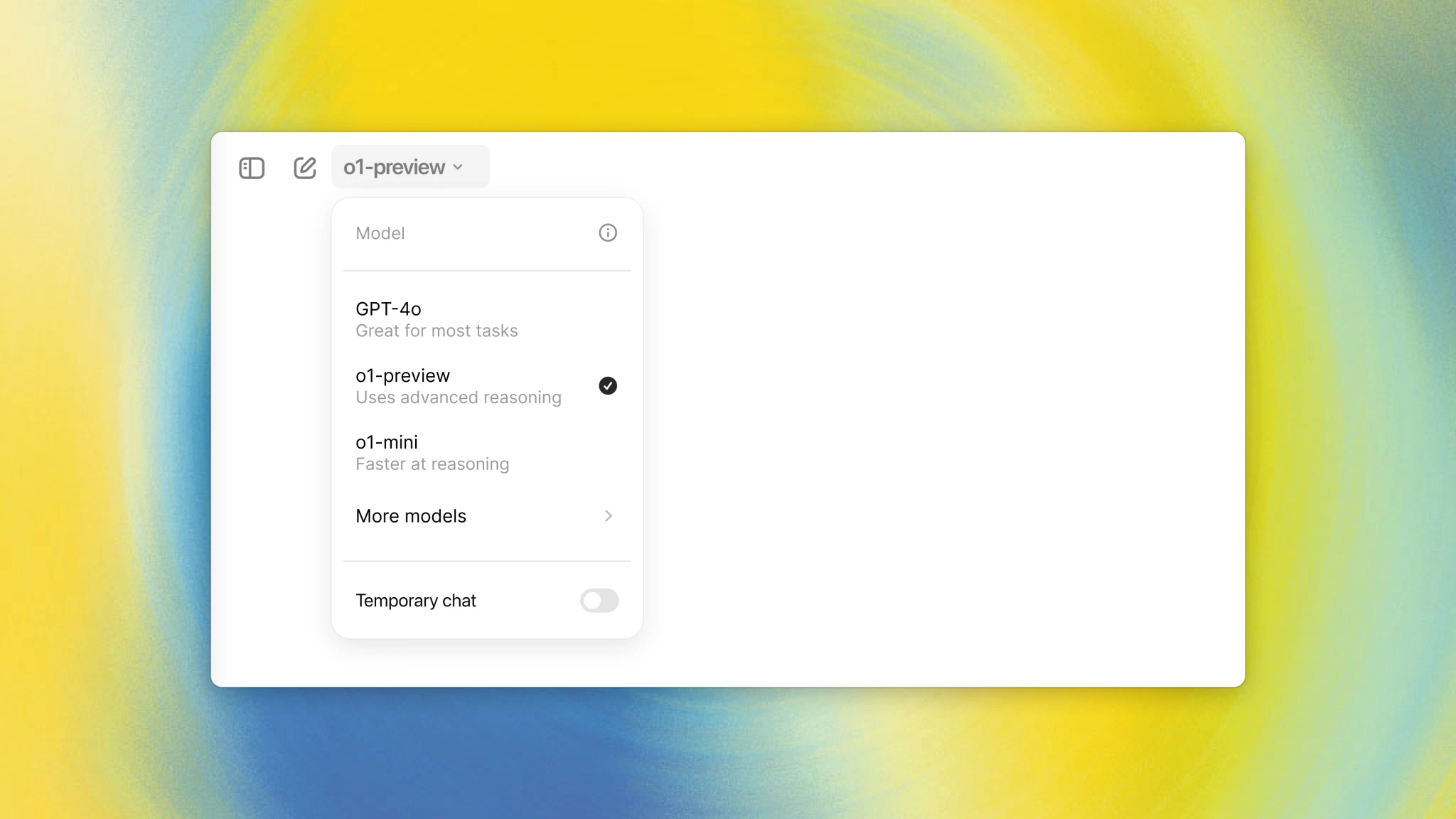 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
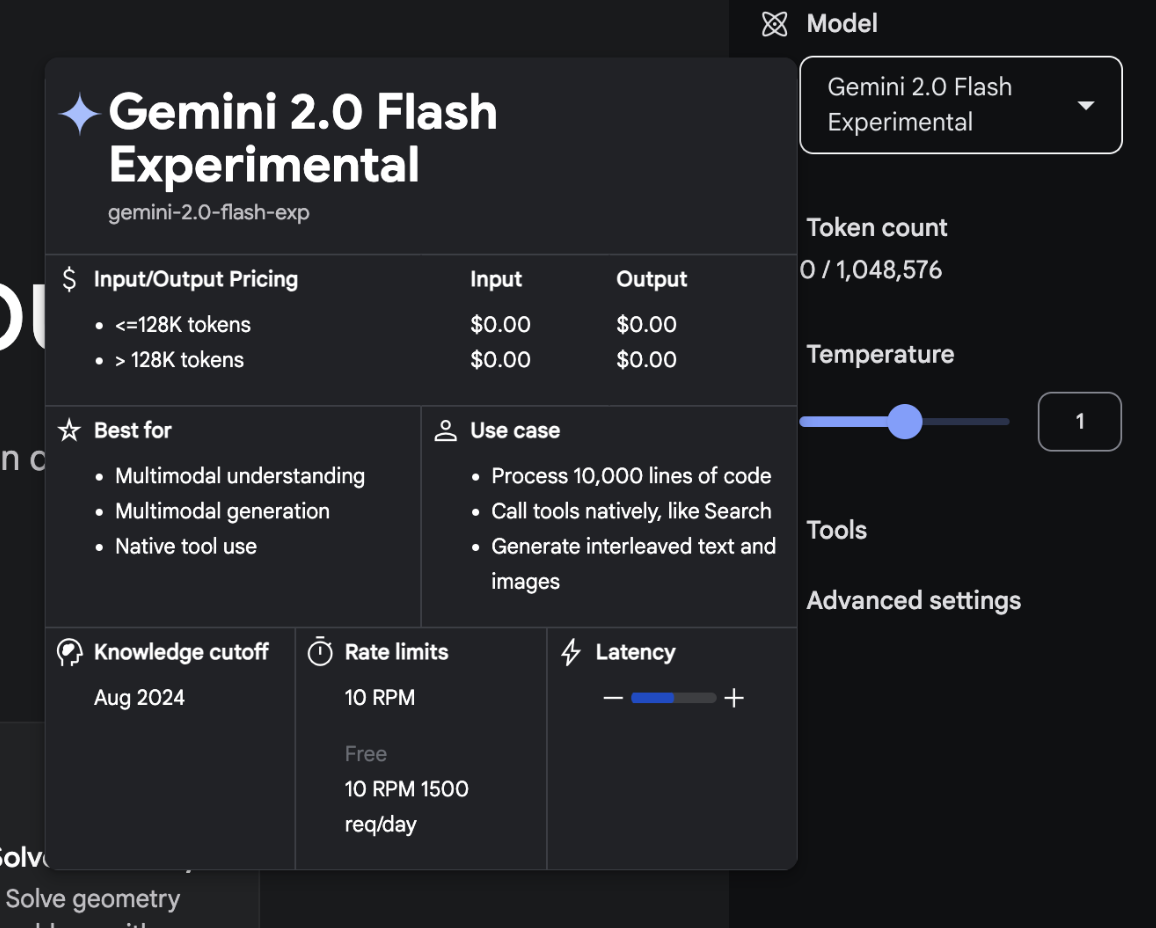 Google AI Studio
Google AI Studio
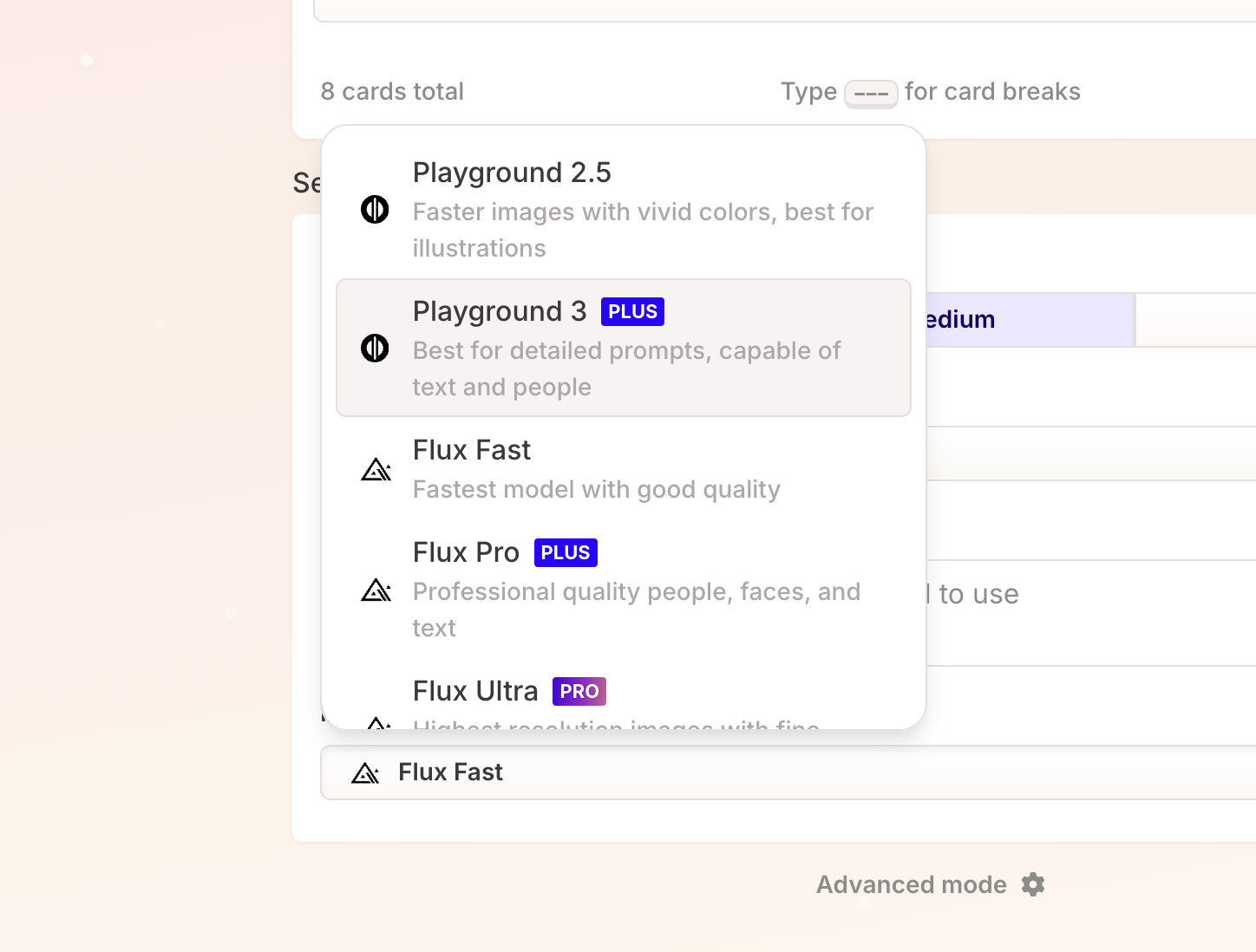 Gamma
Gamma
You can check the next 10 patterns in Part 2.